Introduction
to Online Legal Research (Westlaw and Lexis)
Professor Callister
|
Session:
Fall
- Spring
|
| Lexis:
Shepard's
Citation
Service
Table of Authorities |
L14 |
|
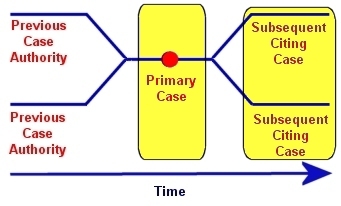 Previously,
you have seen how to Shepardize a specific, primary case (e.g.,
Davis
v. Beason). Previously,
you have seen how to Shepardize a specific, primary case (e.g.,
Davis
v. Beason).
In addition, you have learned how the Lexis version of Shepard's conveniently flags subsequent citing cases (as to whether they have been overruled, criticized, questioned, etc.). Click here to review. Consequently, you can now analyze citations from your primary case forward in time.
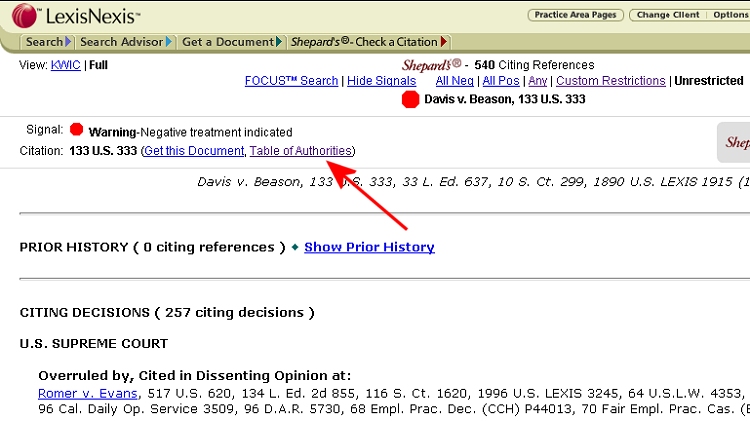
To move back through precedential pedigree, and examine the cases upon which your primary case relies, use the Table of Authorities function. |
|
|
UMKC
School of Law |
|